Contribution of digitalization to overcoming challenges in district heating
Source: eKapija
 Monday, 21.11.2022.
Monday, 21.11.2022.
 23:58
23:58
 Monday, 21.11.2022.
Monday, 21.11.2022.
 23:58
23:58

The concept of integrated management system in the most developed district energy systems in Europe entails modernization, automatization and digitalization of facilities for production and distribution of thermal energy, integrated process management systems, software platforms for real-time system management, software platforms for equipment management and maintenance as well as integrated technical information and business information systems of a company. The latest applications for these processes enable working in web environment, are based on digital platforms, modular, integrated, secure and developed specifically for district energy systems.
The system for supervision and management of remote subsystems (heating sources and heating substations) entails the application of one of the modern distributed digital management systems, data acquisition, interaction with external databases, reporting, managing alarm systems, integration of algorithms and other functions through proper communication infrastructure. In modern district heating systems, the existing supervision and management system is supposed to be integrated with a software platform for technical-economic optimization of the system. Implementation of this tool provides comprehensive insight and control of performance indicators on the heating networks in real time, supports management of thermal energy production and choosing optimal energy mix in real time. Also, this tool allows for reduction of energy losses, production and investment costs. Top level of performance management includes analyzing different development scenarios and their impact on connecting new residential and office buildings to the grid, planning energy requirements, grid reconfiguration and restoration outlines, planning investments for the reconstruction of the existing and the construction of the new distribution network and the like.
In large district heating systems, efficient processing of huge sets of data is only viable with the help of the so-called “big data” digital systems. These data structures are processed with machine learning tools and artificial intelligence algorithms providing fast and competent interpretation of the collected data and support in decision making to system operators. Some of the functions of this tool are predicting possible overheating depending on the weather conditions and choosing optimal technical-economic production balance for covering consumer needs. Optimization algorithms based on predicting thermal energy demand, as a primal condition for screening thermal overloads, predict planned production from renewable energy sources (solar thermal, biomass, heat pumps, geothermal springs, waste heat) in order to create an optimal production mix, efficient distribution of energy through smart grids and rational transfer of thermal energy based on the needs of end-users. Digitalizing district heating systems and operational use of these analytics tools promote optimal management of the smart network at the level of production and distribution of thermal energy as well as improved performance and cost-efficiency.
As the price of energy sources continue to soar and there is an intense need for decarbonization of the system and increasing the share of renewable energy sources in production of thermal energy, these software tools have strategic importance to the modern district heating systems. Fourth generation district heating (4GDH) is a coherent technological and institutional concept, which by means of smart thermal grids assists the appropriate development of sustainable energy systems. It integrates all available energy sources into a singular grid (waste heat and energy from renewable sources) for providing heat supply to low-energy buildings with low grid losses and high energy efficiency. With this technological transformation, which benefits both users and heating companies, we are striving towards implementing smart district heating grids in city zones.
One example of good practice is the solution recently introduced by METRONIK Inzenjering doo from Belgrade (www.metronik.rs), a modular software platform, MePIS Energy, for managing production and information systems of district heating in PUC Beogradske elektane, The software provides functional integration with process databases, data verification, creating predictions of thermal energy demand with weather-based normalization of measurements, designing optimal production plan, balancing thermal energy production in real time, production analysis, alarm notifications and communication with system operators. This production information system operates by completely integrating with the existing information environment of the power plant, namely, exchanging data with the supervisory control systems and business information systems. MePIS Energy provides the total integration of the key data in the thermal energy production system (heating sources and boiler rooms of Beogradske elektrane plants), balance analysis on a hourly, daily, monthly and yearly level, real time communication with the supervisory control system, creating production plans, generating reports, trend and key performance indicators, setting up work modes and exit temperatures and many other functions. The platform operates in a web environment and qualitatively, it is a superlative tool for production management compared to previous types of operation.
Block diagram of MePIS system in Belgrade power plants (Photo: Metronik)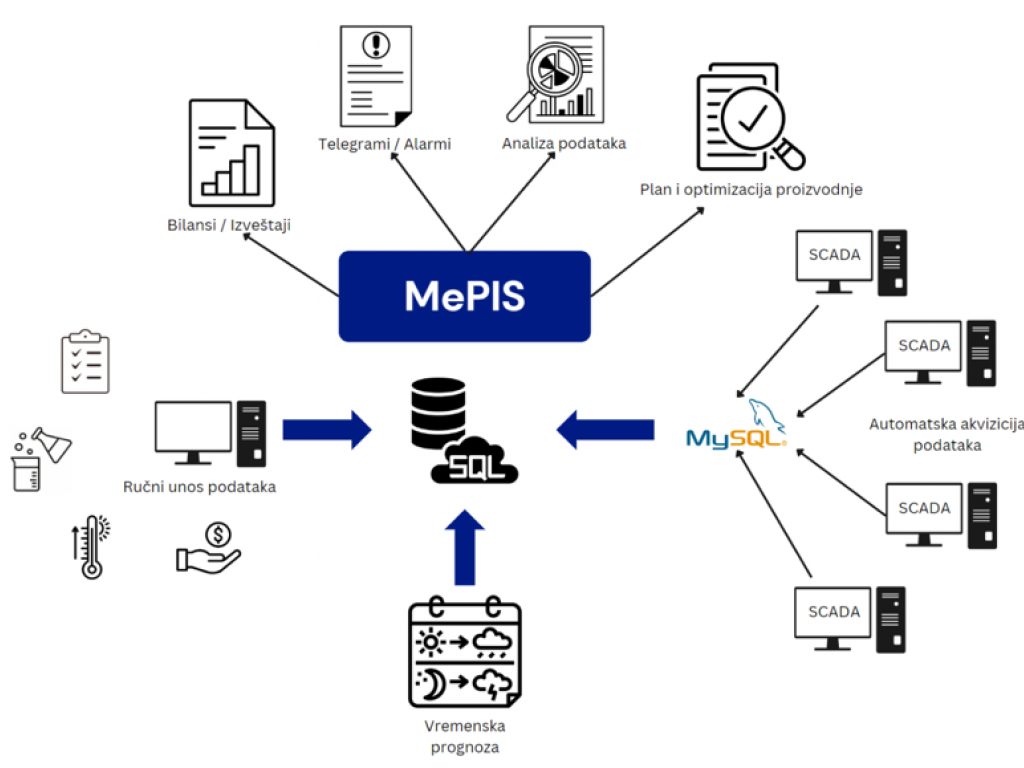

MePIS gathers data from all heating sources and weather forecasts and organizes it into a comprehensible unit. Acquisition of data depends on how digitally developed individual systems are. Less developed systems require manual data input. Collected data is processed, sorted and presented in a simple manner to the end-user while predicting the required amount of thermal energy needed to satisfy user demand. The system generates reports, production balance sheets and alarm notifications which is used to thoroughly monitor production and distribution of thermal energy, energy consumption and generate related predictions.
The data is stored in the MySQL database through automatic acquisition from SCADA systems and is then transferred to MePIS SQL server. Data which cannot be automatically collected, are entered manually with the MePIS software. Weather forecasts send outdoor temperature predictions on the hour and the system decides the energy needed for distribution and the amount of energy sources required for production. MePIS uses the collected data to generate balance sheets on a daily, montly and annual level which are instantly available to the end-user in standard formats (pdf, xls, csv). MePIS also generates alarm notifications and telegrams which are sent to dispatchers and technical services if there`s a change that needs urgent addressing.
The data is stored in the MySQL database through automatic acquisition from SCADA systems and is then transferred to MePIS SQL server. Data which cannot be automatically collected, are entered manually with the MePIS software. Weather forecasts send outdoor temperature predictions on the hour and the system decides the energy needed for distribution and the amount of energy sources required for production. MePIS uses the collected data to generate balance sheets on a daily, montly and annual level which are instantly available to the end-user in standard formats (pdf, xls, csv). MePIS also generates alarm notifications and telegrams which are sent to dispatchers and technical services if there`s a change that needs urgent addressing.
(Photo: Metronik)

Examples of various displays (Photo: Metronik)

Besides developing their own software solutions, METRONIK Inzenjering is system integrator for Leantheat Network, a software platform for technical-economic real time optimization of district heating systems for Danfoss company from Denmark, the biggest global manufacture in the district heating sector.
Companies:
 Metronik Inženjering d.o.o. Beograd
Metronik Inženjering d.o.o. Beograd
 JKP Beogradske Elektrane Beograd
JKP Beogradske Elektrane Beograd
 Danfoss d.o.o. Beograd
Danfoss d.o.o. Beograd
Tags:
METRONIK Inzenjering doo Belgrade
Metronik
PUC Beogradske elektrane
Danfoss
energy consumption in the heating sector
energy consumption in the cooling sector
district heating systems
district heating
optimization of operations
energy crisis
system for supervision and management of remote subsystems
machine learning
artificial intelligence
decarbonization
digitalization
MePIS Energy
Leanheat Network
special edition newsletter
Digital Transformation Roadmap to eFuture
Comments
Your comment
Most Important News
Full information is available only to commercial users-subscribers and it is necessary to log in.
Follow the news, tenders, grants, legal regulations and reports on our portal.
Registracija na eKapiji vam omogućava pristup potpunim informacijama i dnevnom biltenu
Naš dnevni ekonomski bilten će stizati na vašu mejl adresu krajem svakog radnog dana. Bilteni su personalizovani prema interesovanjima svakog korisnika zasebno,
uz konsultacije sa našim ekspertima.


 Izdanje Srbija
Izdanje Srbija Serbische Ausgabe
Serbische Ausgabe Izdanje BiH
Izdanje BiH Izdanje Crna Gora
Izdanje Crna Gora


 News
News











