How to do business in Russian-speaking countries? – You will face obsolete technology, high labor costs, corruption...
The extent to which doing business in Russian-speaking countries is different from doing business in Western Europe was shown at the Kwan Consulting event at the Slovenian Business Club in Belgrade. The topic “Doing Business with Russia and Soviet Union Successor States” attracted interest from business people in Serbia, who were given excellent advice and guidelines, but also presented with what they could expect.
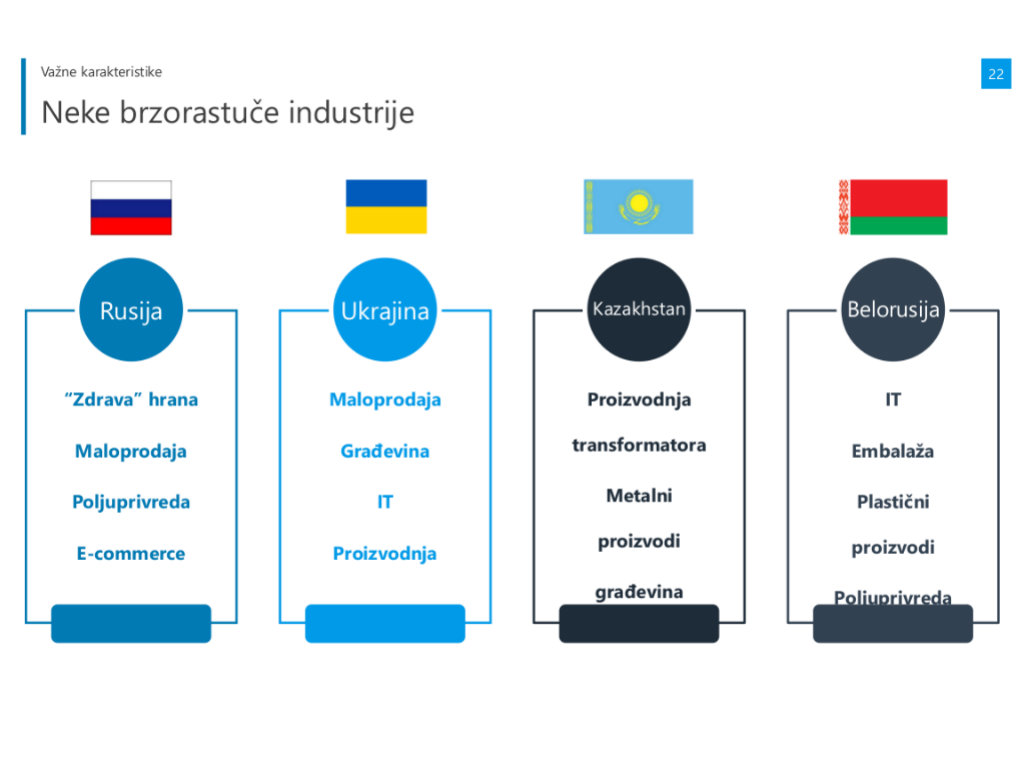
Svyatoslav Biryulin, the founder of the Kwan Consulting company, which specializes in strategic consulting and market research, presented the markets of Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan and Belarus.
Russia
Russia is a country which exports natural resources the most, such as minerals, oil and gas (66.9%). Still, according to Biryulin, this country does not produce as much as it should. The economy is stagnating, and GDP growth is 1%.
– Russia imports a lot, and the import structure has changed considerably since 2014, when sanctions were imposed by the European Union. Cars are imported the most (50.9%), followed by chemical products and food and agricultural products – Svyatoslav Biryulin said.
He added that the import from Serbia had increased as well, but that the biggest exporter to Russia at the moment was China. Merchandise trade between Russia and Serbia amounted to USD 3.06 billion in 2018, which is USD 500 million more than a year before.
He also said that the state tried to stimulate the economy through tenders, which were often closed for foreigners.
There are currently 23,500 foreign companies in this country, the biggest of which are Auchan, Metro, Toyota, JTI, Ikea, Volkswagen, Leroy Merlin, British American Tobacco, Philip Morris International and PepsiCo.
– Most of the income comes from employers from Germany (EUR 17 billion), France (EUR 13.3 billion) and the USA (EUR 12.6 billion) – Biryulin said.
Ukraine
Ukraine is the second biggest country in size and populace in the observed region. As Biryulin pointed out, the economic situation is worse here than it was five years ago, but, on the other hand, there are business opportunities.
– A large amount of corruption is Ukraine's problem, but its economy is market economy to the largest extent compared to all the other countries, because the state play a greater role here. The economy is weak, but has potential. The migration of workers to the EU, especially Poland, is a problem they're facing.
Ukraine mostly exports metals (22.8%) and imports machines and equipment (19.2%).
Svyatoslav Biryulin, the founder of the Kwan Consulting company, which specializes in strategic consulting and market research, presented the markets of Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan and Belarus.
Russia
Russia is a country which exports natural resources the most, such as minerals, oil and gas (66.9%). Still, according to Biryulin, this country does not produce as much as it should. The economy is stagnating, and GDP growth is 1%.
– Russia imports a lot, and the import structure has changed considerably since 2014, when sanctions were imposed by the European Union. Cars are imported the most (50.9%), followed by chemical products and food and agricultural products – Svyatoslav Biryulin said.
He added that the import from Serbia had increased as well, but that the biggest exporter to Russia at the moment was China. Merchandise trade between Russia and Serbia amounted to USD 3.06 billion in 2018, which is USD 500 million more than a year before.
He also said that the state tried to stimulate the economy through tenders, which were often closed for foreigners.
There are currently 23,500 foreign companies in this country, the biggest of which are Auchan, Metro, Toyota, JTI, Ikea, Volkswagen, Leroy Merlin, British American Tobacco, Philip Morris International and PepsiCo.
– Most of the income comes from employers from Germany (EUR 17 billion), France (EUR 13.3 billion) and the USA (EUR 12.6 billion) – Biryulin said.
Ukraine
Ukraine is the second biggest country in size and populace in the observed region. As Biryulin pointed out, the economic situation is worse here than it was five years ago, but, on the other hand, there are business opportunities.
– A large amount of corruption is Ukraine's problem, but its economy is market economy to the largest extent compared to all the other countries, because the state play a greater role here. The economy is weak, but has potential. The migration of workers to the EU, especially Poland, is a problem they're facing.
Ukraine mostly exports metals (22.8%) and imports machines and equipment (19.2%).
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan has a stable economy with potential growth. The country has a market economy, and the corruption is moderate.
– The problem of this country is the existence of clans – said Svyatoslav Biryulin.
Kazakhstan mostly exports minerals (68.7%) and imports machines, cars and equipment (36.5%).
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan is the largest country in Central Asia and the third biggest former Soviet state. The economy is unstable, as a transition towards market economy is currently underway.
– This country has the youngest economy, but it is developing fast, because Uzbekistan is starting out from the point where Russia was in the 1920s. Those are the conditions of doing business, but the opportunities are interesting – Biryulin emphasized.
He added that the degree of business culture was low and that few people spoke English, but that everyone spoke Russian.
– Europeans find Uzbekistan interesting due to the fast development of all industries, but also because a 30-day visa-free regime has been implemented. That shows how interested they are in foreign investments, and it is also a fact that they are adopting laws on incentives for foreign investors – Biryulin emphasized.
The country mostly exports services (24.5%) and imports cars and equipment (41.9%).
Belarus
Belarus has the smallest economy and the most difficult business conditions, even for local companies, so the fewest foreigners operate here.
The problem here is that workers go to Poland and Russia. The state's participation is 40% – Biryulin says.
This country mostly exports minerals (25%), but what's interesting is that minerals also account for the majority of its imports (29.2%).
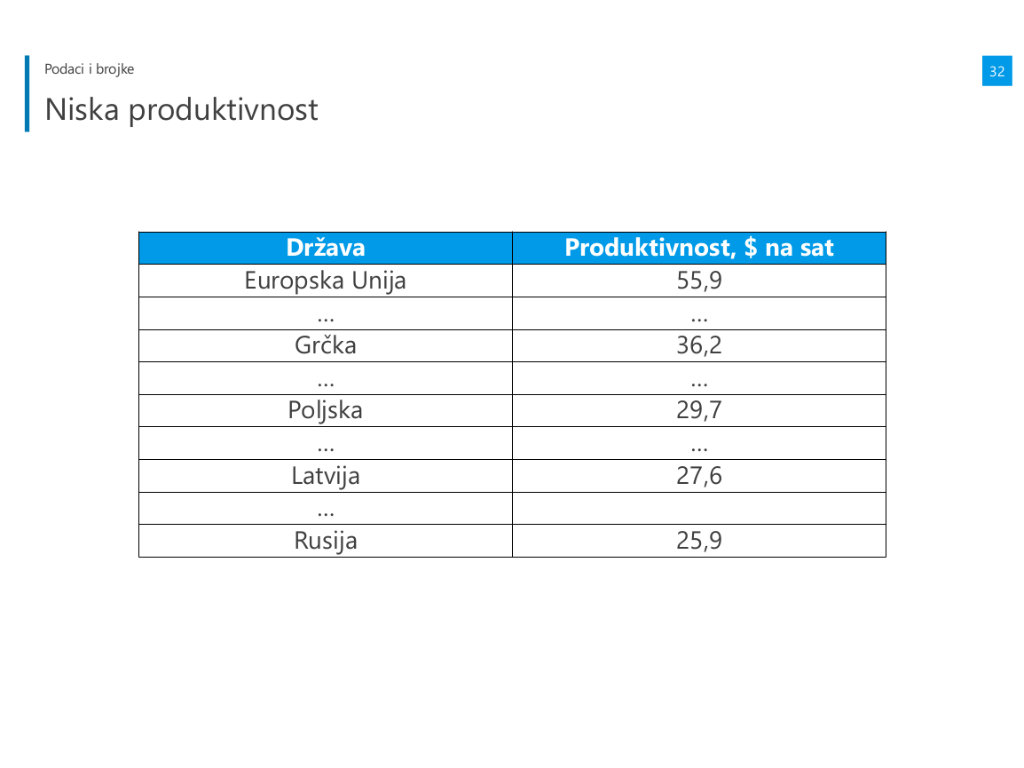
The Russian-speaking area, when it comes to the market is characterized by weaknesses: low productivity, low degree of digitization, high operating costs, high salaries, high interest rates, expensive energy, lack of investments and corruption.
– Companies in this area still use obsolete technologies and obsolete solutions and very little is invested in this. Also, graduates without experience don't want to work for less than EUR 1,000 and workers are lazy too. Russia and Belarus have an interest rate of 13%, in Kazakhstan it is 17% and in Ukraine it is 25%, whereas energy is more expensive than in the USA – says Svjatoslav Biryulin.
He added that it was very hard to find good workers, except in Uzbekistan, but that the said country had a problem of a lack of highly qualified workforce. Labor organization is weak, and outsourcing is nonexistent.
– Manager salaries in Russia start at EUR 1,500, in Kazahstan they start from EUR 1,000, whereas in Ukraine and Belarus they start from EUR 500. Top managers are paid EUR 7,500, EUR 3,500, EUR 2,500 and EUR 2,000 respectively. Directors are paid EUR 15,000, EUR 7,000, EUR 6,000 and EUR 5,000.
– Innovative, authentic and efficient production does well in this market, and companies with automated production have an opportunity – Svyatoslav Biryulin said.
When it comes to renting office space in Moscow, grade A space costs USD 440/m2, B grade is USD 220/m2, whereas C grade is USD 100/m2. In other parts of the state it's much lower, from 20 to 80 dollars.
Customs Union
The Customs Union is the joint economic space consisting of Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia and Kyrgyzstan. Serbia recently signed an agreement on cooperation with the Eurasian Economic Union.
– I don't see any special opportunities for Serbia right now, compared to the previous individual agreements. I'd say that this agreement is more of a political and psychological character. To Russia, it is important in order for the country to expand the market after the sanctions – Biryulin says.
The Customs Union in fact means that, in certain cases, companies do not pay export, import and customs fees. Also, customs control procedures are simplified and limitations to trade between the members are abolished.
Special economic zones
There are also special economic zones in Russia, where tax exemptions are in force. More precisely, customs tariffs on the import of equipment are not paid. The companies operating this way are Yokohama, Armstrong, Kastamonu, Saint Gobain and Daimler.
– Kastamonu, for example, is a Turkish factory which produces laminates. They operate in Tatarstan, which is one of the most developed economic zones – Biryulin pointed out.
Aleksandra Kekic
Only logged-in users can comment.

 Izdanje Srbija
Izdanje Srbija Serbia Edition
Serbia Edition Serbische Ausgabe
Serbische Ausgabe Izdanje BiH
Izdanje BiH Izdanje Crna Gora
Izdanje Crna Gora













 LinkedIn
LinkedIn Email
Email Copy link
Copy link